Source Description :
Dimensions for the GammaMed Plus source are taken from the study by Ballester et al 1, 2. The Plus source consists of a 3.50 mm long 192Ir core with a diameter of 0.60 cm enclosed in a 0.90 mm diameter AISI 316L stainless steel capsule (density of 7.8 g/cm3 ). The tip of the encapsulation is a conical section with a height of 0.183 mm and an opening angle of 68o . The cone is attached to a 0.50 mm long solid cylindrical section followed by a 3.60 mm long hollow section with an inner diameter assumed to be 0.70 mm. Following the hollow section is a 0.30 mm long solid cylindrical section. A total length of 6.0 cm of AISI 304 stainless steel cable (density of 5.6 g/cm3 ) was included in this simulation. The active length of this source is 3.50 mm. The mean photon energy calculated on the surface of the source is 360.47 keV with statistical uncertainties < 0.002% .
Dose Rate Constant - Λ :
Dose rate constants, Λ , are calculated by dividing the dose to water per history in a (0.1 mm)3 voxel centered on the reference position, (1 cm, Π/2), in the 80x80x80 cm3 water phantom, by the air-kerma strength per history factor (scored in vacuo). Air kerma per history is always calculated using a tracklength estimator in a 10x10x0.05 cm3 air voxel located in vacuo on the transverse axis 100 cm away from the source and then corrected (kr2 = 1.00217) for the lateral and thickness dimensions of the scoring voxel to give the air kerma per history on the central axis at a point 100 cm from the source’s mid-point as described in our previous study 3, 4. Low-energy photons emitted from the source encapsulation are suppressed in the air-kerma calculations by discarding all photons with energy less than 10 keV (i.e., PCUT set to 10 keV in EGSnrc). egs_brachy uncertainties are only statistical uncertainties (k=1).
| Author | Method | Λ (cGy h-1 U-1) | Abs. Uncertainty |
| Safigholi et al 5 | 10x10x0.05 cm3 voxel at 100 cm | 1.1100 | 0.0002 |
| Taylor, Rogers 6 | 10x10x0.05 cm3 voxel at 100 cm | 1.115 | 0.003 |
| Ballester et al 1 | extrap | 1.118 | 0.003 |
| Reyes et al 7 | extrap | 1.116 | 0.03 |
| Wu et al 8 | TOPAS MC | 1.110 | 0.001 |
| Pérez-Calatayud et al 9 | HEBD Consensus value | 1.117 | 0.004 |
| Lopez et al9 | Penelope(with e- transport) | 1.111 | 0.002 |
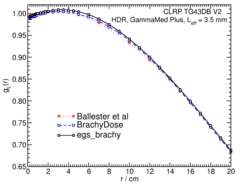
Radial dose function - g(r):
The radial dose function, g(r), is calculated using both line and point source geometry functions and tabulated at 36 different radial distances ranging from 0.2 cm to 20 cm.
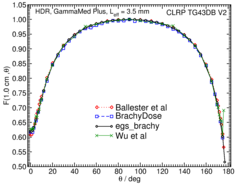
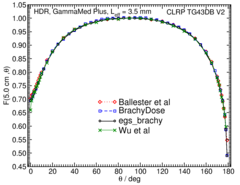
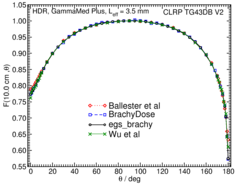
Anisotropy function - F(r,θ):
Anisotropy functions are calculated using the line source approximation and tabulated at 12 radii from 0.25 cm to 20 cm and 47 unique polar angles with a resolution of 5° or better. The anisotropy factor, φan (r), was calculated by integrating the solid angle weighted dose rate over 0° to 180° .
Along-Away Dose Data:
Along-away dose data are tabulated at 16 away distances from 0 cm to 20 cm and 31 along points from -20 cm to 20 cm. Doses are normalized to SK, the air-kerma strength.
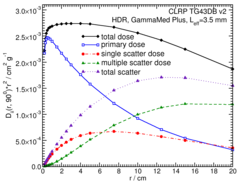
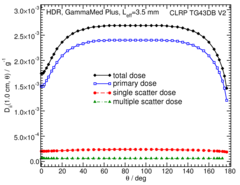
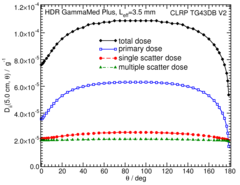
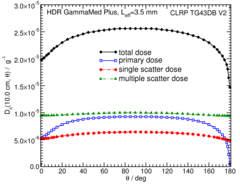
Primary and Scatter Separated (PSS) Dose Data: Dii (r,θ):
Primary and Scatter Separated (PSS) dose data are tabulated at 12 radii from 0.25 cm to 20 cm and 47 unique polar angles with a resolution of 5°or better. High resolution (Δr = 1 mm, ΔΘ = 1°) primary scatter dose data are also available in .csv files. For the purposes of these calculations, any photon escaping the source encapsulation is considered a primary. Only photons which scatter within the phantom are counted in the scatter tallies. Doses are normalized to the total photon energy escaping the encapsulation. The "ii" subscript labeled in the Dii(r, θ) represent the total scatter as Dto(r, θ), the primary photons as Dpr(r, θ), the single scatter photon as Dss(r, θ), and the multiple scatter photons as Dms (r, θ).
Photon Energy Spectra
Photon energy spectra generated by the source model are calculated using the egs_brachy surface count scoring option to get the spectrum exiting the surface of the source. The relative counts here are the counts per 1 keV bin normalized to 1 count total in the spectrum. The MC calculations have a statistical uncertainty less than 0.002% on the mean energy. The spectrum data are available in xmgrace format below.
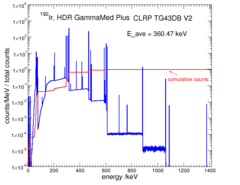
Photon energy spectrum on the source surface: xmgrace
Tabulated data:
Tabulated data are available in .xlsx format: Excel
References:
1. F. Ballester et al , Technical note: Monte-Carlo dosimetry of the HDR 12i and Plus 192Ir sources, Med. Phys., 28 , 2586-2591, 2001
2. F. Ballester et al , Erratum: "Technical note: Monte-Carlo dosimetry of the HDR 12i and Plus 192Ir sources" [Med. Phys. 28, 2586-2591 (2001)], Med. Phys., 31 , 2372-2372, 2004
3. R. E. P. Taylor et al , Benchmarking BrachyDose: voxel-based EGSnrc Monte Carlo calculations of TG--43 dosimetry parameters, Med. Phys., 34 , 445 - 457, 2007
4. D. W. O. Rogers, Inverse square corrections for FACs and WAFACs, Appl. Radiat. Isot.,153 ,108638, 2019
5. H. Safigholi, M. J. P. Chamberland, R. E. P. Taylor, M. P. Martinov, D. W. O. Rogers, and R. M. Thomson, Update of the CLRP TG-43 parameter database for high-energy brachytherapy sources, to be published (Current calculation).
6. R. E. P. Taylor, D. W. O. Rogers, EGSnrc Monte Carlo calculated dosimetry parameters for 192Ir and 169Yb brachytherapy sources, Med. Phys., 35 , 4933 - 4944, 2008
7. E Reyes et al, Monte Carlo characterization of the GammaMed HDR plus Ir-192 brachytherapy source, Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2, 015017, 2016.
8. J. Wu, Y. Xie, Z. Ding, F. Li, L. Wang, Monte Carlo study of TG-43 dosimetry parameters of GammaMed Plus high dose rate 192Ir brachytherapy source using TOPAS' J Appl Clin Med Phys, 22, 146-153,2021
9. Pérez-Calatayud et al , Dose Calculation for Photon-Emitting Brachytherapy Sources with Average Energy Higher than 50 keV: Full Report of the AAPM and ESTRO, 2012 by AAPM, ISBN: 978-1-936366-17-0
10. J. F. A. Lopez et al, Monte Carlo dosimetry of the most commonly used 192Ir high dose rate brachytherapy sources, Rev. Fis. Med. Phys. 12, 159-168, 2011